Crypto Wallets — the gate for web3
Nowadays, crypto wallets are crucial to step into decentralised web3 world. Without it, it is hardly impossible to sign in or approve any…

Nowadays, crypto wallets are crucial to step into decentralised web3 world. Without it, it is hardly impossible to sign in or approve any transaction, data recording, etc. As we know and follow the latest news about blockchain, crypto assets can open doors to not only super secured and safe transactions, but also decentralised health records, polling and voting in elections.
Agenda:
- Intro,
- Definition,
- Impact of blockchain network on wallets,
- Private key,
- Public key,
- wallet as a gate for dapps,
- Types of wallets,
- Paper wallets,
- Hardware wallets,
- Online wallets,
- Examples.
Definition
Crypto wallet store your private key which is necessary to prove that you are the owner and also sign transactions. What is worth to mention, crypto wallets are not like normal ones, but digital. There is one main difference. Your holdings are not stored by wallets, because hey “live in blockchain”. Wallet just proves that it is yours.
Another key used by wallets is a public key. Considering that wallet is like an email account, public key is an address, private key is the password. Everyone who wants to send somebody mail, he needs to know correct email address. In crypto if the user wants to send assets to other wallet, it is needed to input public key of the wallet.
Impact of blockchain network on wallets

In using crypto wallets it is highly important to send assets through one network. For example, sending eth (Ethereum blockchain coins) on public key of Solana blockchain can cause losing holdings. It is needed to check if wallet has the same public key for different cryptocurrencies.
Ecosystems which grew as a scaling platform on for example Ethereum, use the same pair of keys. Polygon network is the perfect example, it was build as a layer of ethereum, but uses own coins (MATICs). It was build to decrease fees, but still is connected with ethereum ecosystem.
Private key
Private key is the variable in cryptographic that encrypts and decrypts data. Note that to have safe assets, private key must be known only for the owner of the data/holdings.
More about public and private keys soon. in thread about asymmetric encryption.
Public key
Public key is the large numeric data which allows to receive assets. It is mathematically paired with private key which signs transactions.
Wallet as a gate for dapps
Crypto wallets can be understood as. “the gate for web3 world”, but why?
In web3, decentralized apps (dapps) enables authentication process not like standard Web2 apps through email, social media, but through crypto wallets. You log in with wallet and approved this by signing with private key.
It is a revolutionary solution, because all the credentials are stored by user side, not in centralized databases of platform owner.
Types of wallets:
- paper wallets,
- Hardware wallets,
- Online wallets.
Paper wallets
Keys are written on a physical medium like paper, then stored in a safe place. It is one the most secured way, but harder to use, because sending coins can be proceeded only by the Internet and keys needs to be correctly input.
Hardware wallets
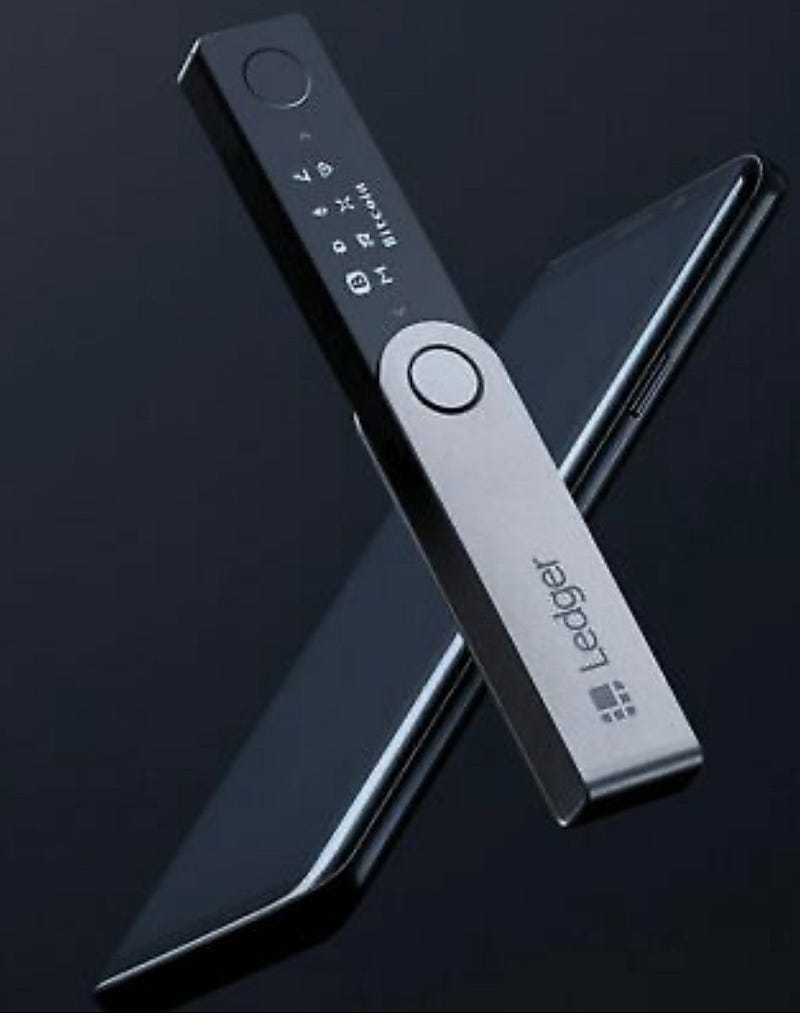

Keys are stored in thumb-drive device that is kept in a safe place. This device is only connected to a computer when there is need of using crypto. Idea of using this kind of wallets is to balance security and convenience.
Online wallets
In this case, keys are stored in app or other software. It is more user friendly but also easier to hack. Using crypto is as easy as using online bank account.
Examples of wallets

There are plenty of wallets available across the web3 world. There can be used as a browser extension and mobile application. The most popular ones are:
- metamask,
- rainbow,
- coinbase wallets,
- gnosis safe,
- math wallet.




